Professor Zhao Weilian from the Institute of Hematology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University, is a team of researchers on peripheral lymphoma. Recently, the team used ChIP-seq combined analysis to reveal the mechanism of action of cidabenamine and decitabine on peripheral lymphoma with histone modification gene mutation. The research results were published monthly in the authoritative journal Heematologica (influence factor 7.7). ( ChIP-seq and mRNA-seq are all provided by Yunxu Biotechnology )
Research Background:
Due to different morphological and immunological characteristics, approximately 50% of peripheral lymphomas (PTCL) cannot be classified and present poor clinical performance, so there is an urgent need to find operational biomarkers for clinically better treatment strategies. Epigenetic changes are known to play a key role in tumor development. Histone modifications, especially methylation and acetylation, are generally involved in the regulation of chromosome status. In this study, the authors first screened for a series of histone modification-related gene mutations by targeted sequencing, followed by ChIP-seq and mRNA-seq to further analyze the combination of cidaben and decitabine for histone modification. Mechanism of action of genetically mutated peripheral T lymphoma.
Research ideas:
First, the authors screened for several key gene mutations, such as histone methylation-related genes (KMT2D, SETD2, KMT2A, and KDM6A) and histone acetylation-related genes (EP300 and CREBBP), and in 125 cases. Of the 45 patients with PTCL, there were 59 individual cell mutations. Clinical studies have found that histone modification-related gene mutations are associated with lower progression-free survival in patients without chemotherapy and increased sensitivity to the histone deacetylase inhibitor cidabenamine.
The authors found that the histone deacetylase inhibitor cidabenamine combined with the hypomethylating agent decitabine significantly inhibited the growth of EP300-mutant T lymphoma cells and the growth of KMT2S mutant T lymphoma cells. The authors further revealed the mechanism of action of cidabenamine and decitabine on peripheral T lymphoma with histone modification gene mutations by ChIP-seq and mRNA-seq ( ChIP-seq and mRNA-seq are both from cloud-like organisms). Provide technical services ). Decitabine can synergize with sidabenamine to enhance KMT2D interaction with transcription factor PU.1, regulate H3K4me-related signaling pathways, and enhance the sensitivity of PTCL to sidabenamine. In the KMT2D mutant transplanted T lymphoma model, the combination of citapilin and decitabine significantly delayed tumor growth and induced apoptosis through KMT2D/H3K4me.
1. Statistics of peripheral T lymphoma mutations
The authors enrolled 239 untreated PTCL patients and targeted sequencing of available tumor samples from 125 patients. The authors found in 125 patients, 60 of them had a total of 91 somatic mutations in the epigenetic modification gene. Most of the mutations were missense mutations (n=72), as well as nonsense mutations (n=10) and frameshift mutations (n=9). The results showed that similar to other tumors, the SNV map was more biased towards C>T/G>A mutation, which was not related to age and gender. Histone methylation-modified gene mutations occur in KMT2D (encoding H3K4 methyltransferase, 25/125, 20%), SETD2 (encoding H3K36 methyltransferase, 6/125, 4.8%), KMT2A ( H3K4 methyltransferase, 3/125, 2.4%) and KDM6A (encoding H3K27 demethyltransferase, 1/125, 0.8%), and no EZH2 mutation. The histone acetylation modification gene mutation occurred in EP300 (encoding H3K18 acetyltransferase, 10/125, accounting for 8%) and CREBBP (encoding H3K18 acetyltransferase, 5/125, 4%). There are other DNA methylation genes and mutations in chromosome remodeling genes. According to the classification of mutant genes, these four rarely overlap, especially the histone methylation modification gene mutation and histone acetylation modification gene mutation, which indicates that histone modification genes may play a role in different biological processes.
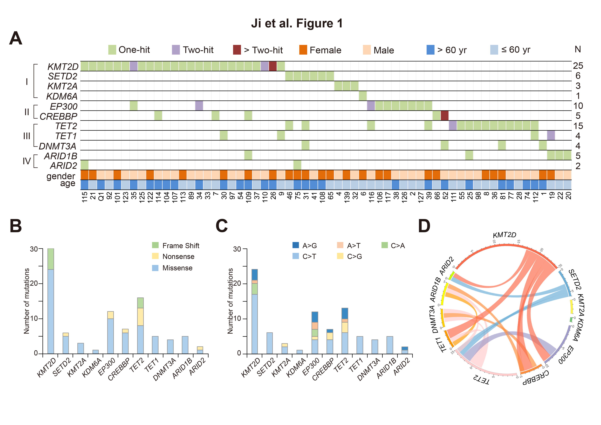
Figure 1: PTCL mutation classification
2. Histone modification gene mutation makes T lymphoma cells more sensitive to cidabenamine and or decitabine
The KMT2D and EP300 missense mutant plasmids were transfected into JurKat cells, respectively, and it was found that the KMT2D mutation inhibited the expression level of H3K4me3, but was restored by the histone deacetylase inhibitors romidepsin and cidabenamine. In addition, the EP300 mutation inhibits the expression level of H3K18ac, but is restored by the histone deacetylase inhibitors valproic acid, rosolic acid or romidepsin and citadine. KMT2D mutations were also found to significantly reduce the expression of H3K4me3 in the nucleus (30%) in PTCL tumor samples, and the EP300/CREBBP mutation also significantly reduced the expression level of H3K18ac in the nucleus (17%). Interestingly, 30 mg of citapilamine was administered orally to a mutant patient twice a week, and patients with relapsed histone-modified gene mutations were completely or partially relieved. This result suggests that these mutations may make PTCL patients more sensitive to histone deacetylase inhibitors. 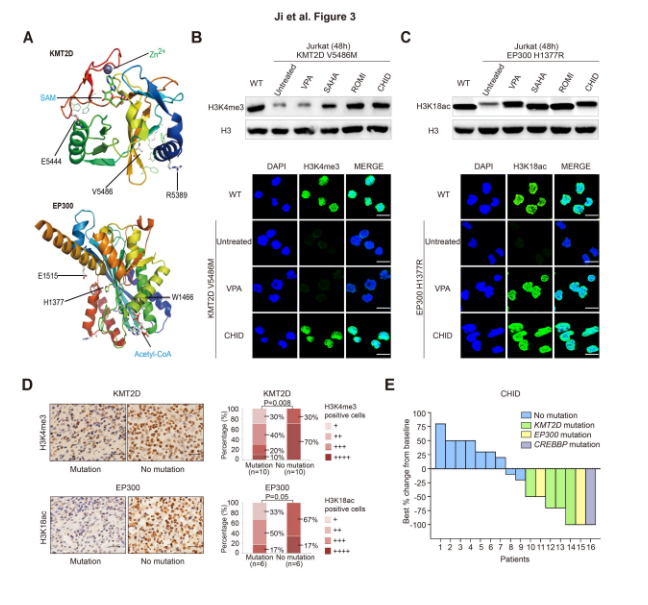

Schematic: Effect of histone acetylation inhibitor on KMT2D mutation and EP300 mutant PTCL
This conclusion was further confirmed by in vitro experiments. Flow cytometry demonstrated that citalopram and decitabine synergistically induced apoptosis and G0/G1 arrest in KME2D mutations. In the KMT2D mutant transplanted T lymphoma model, the combination of citapilin and decitabine also significantly delayed tumor growth. In vitro and in vivo experiments consistently showed that the combination of citapilin and decitabine was more pronounced than the drug alone.
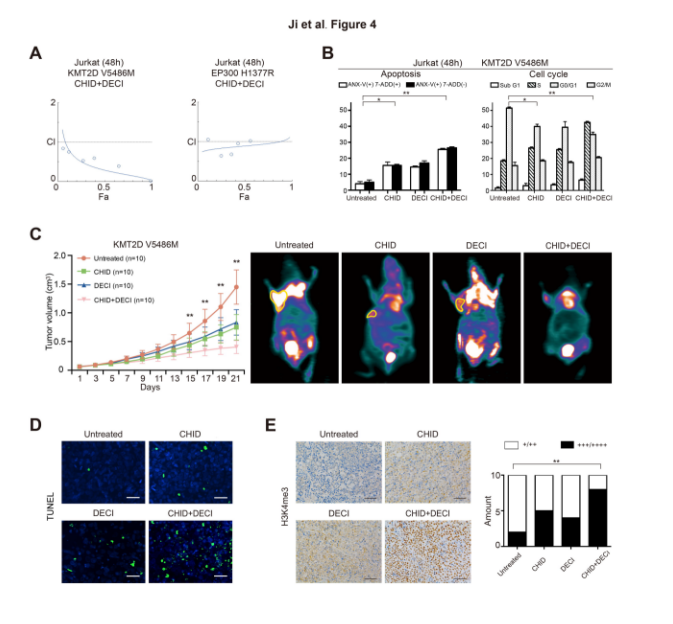
Figure: Effect of cidaben and decitabine on KMT2D mutation and EP300 mutant PTCL
3.ChIP-seq combined with mRNA-seq reveals the mechanism of action
To clarify the target gene for KMT2D-H3K4me3 DNA binding, the authors used ChIP-seq to detect H3K4me3-bound target genes in KMT2D mutant cells treated with citapilin alone or in combination with decitabine. The Venn map indicates that there is a significant non-overlapping region in the promoter region of H3K4me3 binding in combination and drug use. Interestingly, only the combination of cidabenamine and decitabine can affect the expression of the gene promoter of H3K4me3 binding, and the binding of this binding domain is in the region that binds to PU.1 (activates bone marrow or B lymphocytes). Gene expression of the transcription factor). mRNA-seq also showed that the combination is involved in the regulation of multiple cancer signaling pathways, including apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, cell adhesion and transcriptional regulation, compared to the untreated and monotherapy-treated groups, while PU.1 is also involved in cancer. Signaling pathways and transcriptional regulation. The authors further performed GSEA analysis on the overlapping genes in the combination drug-seq and ChIP-seq, and found that the combination of drugs deactivated the MAPK pathway and p-ERK was up-regulated. 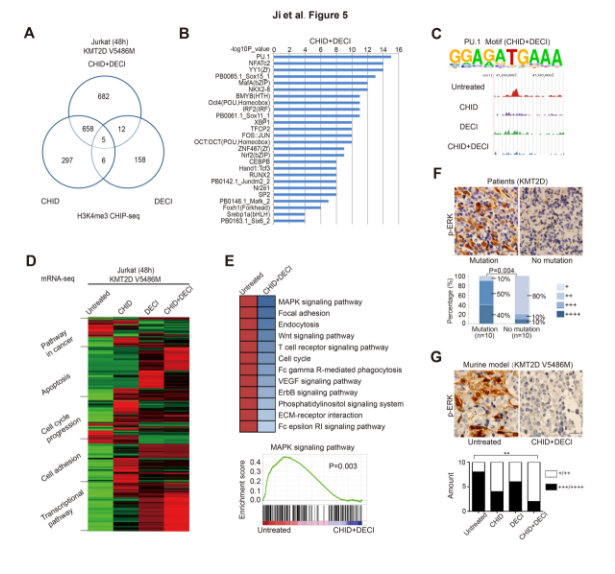

Schematic: ChIP-seq and mRNA-seq reveal the mechanism of PTCL effect of cidabenamine and decitabine on KMT2D mutation and EP300 mutation
References: Histone modifier gene mutations in peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified.
Cloud order related product recommendation:
Cloud sequence biological CHIP sequencing
Cloud sequence biological whole transcriptome sequencing

Shanghai Yunxu Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Â
Shanghai Cloud-seq Biotech Co.,Ltd        Â
Address: 6/F, Building 71, Lane 1066, Qinzhou North Road, Caohejing High-tech Development Zone, Shanghai Â
Telephone website: Â
mailbox:
Veterinary Soluble Powder,Veterinary Water Soluble Powder,Veterinary Drug Soluble Powder,Veterinary Medicine Soluble Powder
NANYANG CHENGPENG PHARMACEUTICAL CO.,LTD , https://www.chppharm.com