Release date: 2016-08-18
The beneficial aspects of physical activity are not necessary to describe, and can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, breast cancer, depression and bone and joint diseases. The World Health Organization recommends that adults need to perform at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise every week.
Ankle fractures have a high incidence in all age groups, and their treatment involves a period of braking to promote bone healing. Pain and stiffness are common complications after ankle fracture. Many patients with ankle fractures still have corresponding dysfunction within 2 to 3 years after fracture. In such patients, the impact of fractures on physical activity, sitting time, and the recovery process of physical activity is still unknown.
Therefore, in order to assess the recovery process of physical activity in patients after ankle fracture, and to compare this group with the general population, observe the reduction of active physical activity and the increase in the meditation lifestyle. Beckenkamp of the University of Sydney in Australia designed the research and published the results in the online journal June J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.
This study was a longitudinal observational cohort study. Subjects who underwent an ankle fracture were enrolled in a randomized controlled trial. The investigators used an International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ-SF) to assess subjects with these ankle fractures. When the brake is released, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months after the release. The investigators also assessed the recovery of physical activity in patients by calculating the total metabolic equivalent (MET) minutes per week.
At the same time, the researchers also calculated the sitting time (how many minutes per day) and the proportion of subjects who met the WHO guidelines for physical activity.
A total of 214 patients with ankle fractures were included in the study. At 1 month after the brakes were removed, the investigators observed an increase in physical activity (from 99 MET minutes/week at the time of braking to after disarming). 979 MET minutes/week) (Figure 1). After the brakes were removed, only 22% of patients with ankle fractures achieved the intensity of activity recommended by the World Health Organization guidelines. In contrast, in the general population, 80% achieved this intensity. The difference was statistically significant. And as time goes by, the difference between the two groups is gradually disappearing.
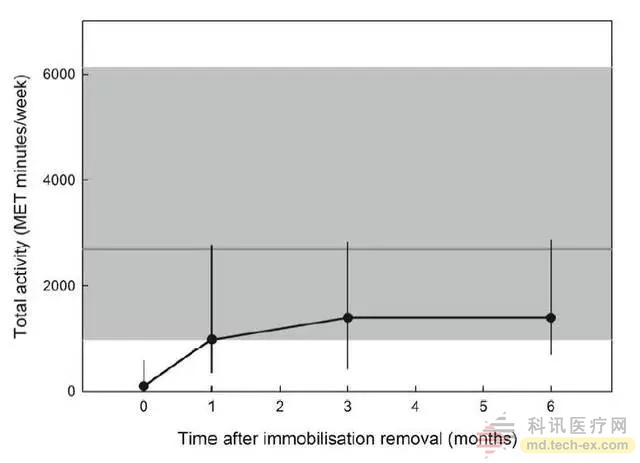
Fig.1 Changes in overall activity intensity at different time points after braking is released
Figure 1 In terms of sitting time, subjects with ankle fractures are longer than the normal group at any point in time.
The results of this study indicate that in the group after ankle fracture, their active physical activity is reduced and the degree of meditation is higher than that of the general population. Therefore, it is necessary to take corresponding countermeasures to increase the physical activity of this group in view of the above situation. The level of evidence in this paper is level 4 of the prognosis study.
Source: Lilac Garden
Garlic Granules,Granulated Garlic,Granulated Garlic Powder,Granulated Garlic To Garlic Powder
shandong changrong international trade co.,ltd. , https://www.changronggarliccn.com