The SWATH (Sequential Window Acquisition of all THeoretical Mass Spectra) acquisition model is a new technology based on mass spectrometry technology jointly developed by scientists from the Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich and AB SCIEX (the world's leading life science analysis technology company). Using this technology, scientists have the first to obtain data for each peptide in a separate proteomic sample analysis.
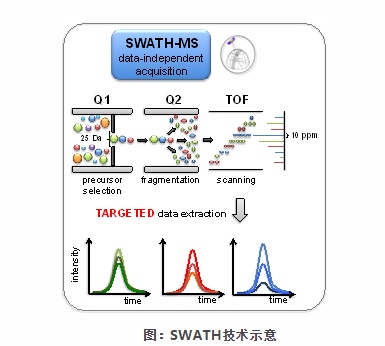
Q: What is the principle of SWATH technology?
A: SWATH is an extension of MS/MSALL technology. Its acquisition mode is a new MS/MS scanning technology. The scanning range is divided into a series of intervals separated by 25Dalton. Ultra-high speed scanning is used to obtain all ions in the scanning range. All fragmentation information.
Q: What are the characteristics of SWATH technology?
A: High sensitivity - SWATH technology inherits the MRM data acquisition mode, combined with the high-resolution Triple-TOF 5600 plus mass spectrometry system, with comparable sensitivity to MRM;
High reproducibility - the quantitative correlation between repeated samples can reach 0.99 or more;
Quantitative accuracy is high – quantitative accuracy is almost equivalent to MRM technology;
Wide linear dynamic range - the quantitative range can span 4 orders of magnitude;
Q: What can SWATH technology be applied to?
A: SWATH technology can be used for proteomic quantification, identification of protein complexes, and analysis of host proteins (HCPs).
Proteomic quantification—The study of protein expression levels in cells, tissues, or organs at different times and under different conditions. The search for biomarkers requires identification and quantification of proteins. The SWATH quantification method is based on the extraction of the peak area of ​​the transition to calculate the peptide content, and the method of inferring the protein content by the peptide content. Quantitative application of SWATH to the proteome-wide level produces the SWATH Quantitative Proteome, which allows rapid identification of differential proteins between several samples.
Identification of protein complexes - Among all cellular functions, protein-protein interactions are the most basic activities. TAP technology is used to specifically enrich the interacting proteins of the target protein, and then combined with SWATH, which has high sensitivity, high accuracy and high throughput, can accurately and accurately enrich the specificity of the target protein. Acting protein to achieve accurate identification of complex proteins.
Host Protein (HCPs) Analysis - Mass Spectrometry enables fast and efficient analysis of HCPs while ensuring better accuracy. The TripleTOF system works with SWATH acquisition mode to analyze HCPs, enabling comprehensive and accurate quantitative analysis while obtaining MSMS information. Quantitative analysis of any number of HCPs was performed and the ppm level HCPs were determined in a 30 minute LC gradient.
Q: What about iTRAQ, SILAC and SWATH?
A: The iTRAQ quantitative proteome method, which does not rely on samples, can quantify the difference in total protein of any sample, and is quantitatively accurate. SILAC is only suitable for cell-level proteomic quantification. The quantification of tissue needs to be explored or the model that has been explored by the predecessors. It is difficult to test new tissues in the middle, and the SILAC culture cost at the cell level is higher. SWATH is a quantitative model related to the target proteome. SWATH can quantify thousands of proteins with high accuracy and flux much higher than MRM. SWATH is very effective for subcellular structures, bacteria, fungi, cell secretions and other samples. it is good. SWATH itself has no bias towards species, and it is also a kind of target protein quantification. The quantitative results are accurate and can be compared with MRM, and the article is more convincing.
Q: What are the requirements for samples using SWATH technology?
A: Using SWATH technology, the sample species is required to have a genomic sequence, an ESTs sequence or a protein reference sequence, which is suitable for detecting samples with low complexity such as bacteria, and the sample protein content is generally at least 10 ug.
Q: What is the difference between “repeating the sample†and repeating the technology and repeating the machine? Published articles generally require several repetitions?
A: The general article will require 2 or 3 experimental repetitions. It is risky to make only one experiment, because if there is a problem in the experimental process, the lack of evaluation of the results is often not convincing enough to affect the publication of the article.
The main purpose of technical duplication is to verify the stability of the test procedure. When the results of the three superior repeats are consistent or similar, we can determine that the processing of the sample is stable. The main purpose of repeating the machine is to verify the stability of the instrument. When the results of the three machines are close or consistent, we can determine that the performance of the mass spectrometer is stable. Current on-board repetitions are still visible in some JPR and MCP articles, that is, the early habits are followed. In the application-oriented article, there is no hard and fast rule on the machine repeat or technical repetition. If you do, of course, the Editor will not find your problem here.
Q: What is the best way to build an ion database when doing SWATHTM data processing?
A: The workflow for SWATH targeted data processing is now very simple, requiring only the parental ion m/z, the m/z and relative abundance of the major fragments, and the retention time. Currently, the establishment of an ion database mainly uses two strategies: DDA acquisition data protein identification or from an external database. In the first method, the sample is collected by the information-dependent acquisition method (DDA), and the protein is identified by ProteinPilotTM software or other search engine, and the identified polypeptide is an ion database for SWATH data processing. Choosing a 1D LCMS or 2D LCMS technology route depends on the complexity of our research object database. With bioinformatics methods, it is also possible to perform targeted protein analysis on MSMS data from external databases while creating an ion database, where retention time correction is required.
Q: What is the best strategy for retention time correction when collecting data via the SWATHTM method?
A: When processing data through SWATHTM software, it is necessary to determine a reasonable narrow retention time window to avoid selecting the wrong peak. There are now two strategies for correcting the difference between the actual observed retention time and the retention time in the database. The retention time is corrected by adding a peptide standard to the sample for database construction and SWATH data collection, or using some of the known medium/high abundance polypeptides present in the sample as a reference.
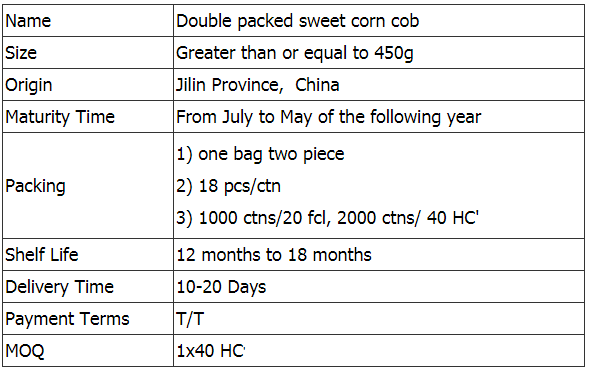
Ready-to-eat Double Packed Sweet Corn
In this category is sweet corn from Jilin Province Agricultural Sister-in-law Food Co.
The physical characteristics of maize consist of grain colour, grain shape, seed coat lustre, grain length, grain width, 100 grain weight, grain diameter, uniformity of the seed and hardness. In most cases, the colour of the endosperm of mature maize kernels is yellow or white, while the seed coat and paste layer are colourless and transparent. Depending on the colour of the kernels, there are three types of maize: yellow, white and mixed. Depending on the kernel form, hardness and different uses, maize is divided into two types: common maize (hard, intermediate, horse-tooth, hard-horse, horse-hard) and special maize (high-lysine maize, high-oil maize, sweet maize, cracked maize, glutinous maize).
The sweet corn of Jilin Province Agricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. belongs to the special corn category of yellow corn.
Also known as fruit corn. The leaves on the outside are light green (only the ears are in the pack, we have removed the leaves for you) and the kernels inside are white or yellow. Sweeter than regular sweet corn, but lower in starch and rich in vitamin E and fibre, which is anti-ageing and aids digestion. Perfect for eating raw, mixed with vegetables in salads; it can also be steamed, but don't cook it for too long, about 5 minutes.


If you have any questions, please contact us directly. If you have any questions, please email us directly.
Delectable Sweet Corn Cob,Microwave Sweet Corn Cob,Country Sweet Corn,Ready To Eat Sweet Corn
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nscorn.com