Who is the super fungus that ravages the world?
April 17, 2019 Source: Science Courtyard
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];The resistance of bacteria is a topic that everyone is very familiar with. Some elementary school students know that some of the "scarred heads" of pathogenic bacteria may be resistant to antibiotics due to mutations. It is also based on the current situation that "all people know a little noun, but few people do fully understand the truth." When people mention antibiotics, they immediately think of "abuse" and "drug resistance". When using antibiotics, they are also cautious. Has become a bird of surprise.
However, the topic of bacterial resistance has not yet been clarified, and resistant fungi have debuted. On April 6, 2019, the New York Times reported a fungus called Candida albicans with the introduction of "Fatal Fungus, No Treatment". This fungus has appeared in various parts of the world in just 10 years, and is still uninterrupted. About half of the infected people die within 90 days, and the final mortality rate is 60%. At present, there are still no specific drugs, and even the world's top medical institutions can do nothing.
 A screenshot of the New York Times report on deadly fungi (Source: author)
A screenshot of the New York Times report on deadly fungi (Source: author) So, when did this terrible mysterious fungus begin to appear? What are the incentives that have led to their simultaneous emergence around the world? This time the pot is antibiotics back? Will such a high mortality rate cause a serious disaster like the Black Death in the Middle Ages? Behind the mystery, in addition to sighing the stubborn survival instinct of small creatures, the complex and subtle interaction between humans and the environment and other creatures makes people think hard.
Fungus? bacterial? virus?
Before the story of resistant fungi begins, it is necessary to review the three microorganisms that have been studied in the junior high school biology class.
First, structurally, viruses are the simplest, bacteria are second, and fungi are more complex than bacteria. If the virus is like a human flatbed, then the bacteria are at least three rounds of electricity, and the fungus may have to be a car.
Second, all three can cause illness in humans and require different approaches to treatment. Most antibiotics are only for bacterial infections, viral diseases require antiviral drugs, and fungal infections have corresponding antifungal drugs.
For example, since the virus has a simple structure, does not have a cell wall, and does not synthesize a protein by itself, an antibiotic that attacks the cell wall or blocks protein synthesis as an antibacterial means cannot act on the virus. In addition, not all antibiotics can target a variety of bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which has a small opening in the cell wall, and many antibiotics cannot penetrate into the interior, so its killing effect is limited.
 a wide range of antibiotics
a wide range of antibiotics Finally, although there are “big enemies†that endanger human health, there are also allies who are indispensable to human life. A variety of fungi are indispensable in the brewing and fermentation industries. Many bacteria play an important role in human digestion and the material circulation of the biosphere. There are also bacteriophages in the virus that can help humans kill bacteria or help humans to synthesize proteins.
Super fungus that ravages the world: Candida albicans
Next, let us uncover the true meaning of the resistant fungus Candida albicans. Candida albicans can cause invasive candidiasis, such as candida bacteremia, pericarditis, urinary tract infections and pneumonia. It is also known as "super fungus" due to its multi-drug resistance, high lethality, and difficulty in diagnosing infection. Currently, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has listed Candida albicans on the “emergency threat†list.
In 2005, Japan organized a scientific research force to conduct a centralized survey of fungal communities in the country. At that time, medical staff from the Tokyo Health and Longevity Medical Center collected a sample from the ear canal of a 70-year-old Japanese woman. During the analysis and identification process that continued for many years, the scientists found that the sample could not be classified into any existing fungus. Thus, Japanese scientists first reported this new fungus named "Cornococcus Candida" in 2009. Unexpectedly, after that, serious cases caused by Candida albicans infection broke out in many countries in Asia and Europe.
 Candida albicans
Candida albicans The first case in the United States occurred in 2013, when a hospital in New York treated a woman with a private complaint of respiratory insufficiency. The 61-year-old woman born in the UAE was positive for Candida albicans one week after admission and eventually died shortly after. However, in view of the fact that Candida albicans has not had such a large influence at present, the hospital did not report the situation until the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention received a case report from the hospital in 2016.
What really made Candida albicans begin to enter the public eye is the infection that broke out in 2016 at the Royal Brompton Hospital in England. At that time, the hospital had 72 cases of infection at one time, and the ICU was closed for two weeks. Due to the initial estimation of the seriousness of the situation in the hospital, the situation in the hospital was not disclosed to the public in the first time.
However, according to the post-disclosure situation, the hospital has issued relevant warnings in the early months before the large-scale intervention of the media, and tried to sterilize the areas where the epidemic occurred. The operator sprays a hydrogen peroxide solution near the area where the fungal patient is infected with a special aerosol. In theory, the vapor of the spray will soak into every corner of the room.
These rooms maintained a saturated state of hydrogen peroxide mist for a week, after which the researchers placed a watch glass in the center of the room and observed the growth of microorganisms in the bottom medium. It is terrifying that even so, there is still a Candida albicans community that appears in the culture dish. However, this incident was eventually concealed by the hospital...
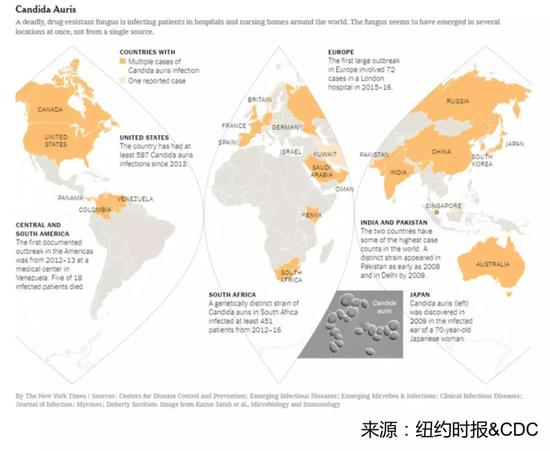
In the past five years alone, Candida albicans has appeared in hospitals in the United States, Spain, Venezuela, India, Pakistan, South Africa and even China. Among them, the large-scale infections in the University Hospital of Valencia in Spain are the most tragic. A large hospital with 992 beds had a total of 372 infections at the time, of which 85 had candida bacteremia and 41% died within 30 days.
Eruption almost simultaneously in many places: the mysterious origin of resistant fungi
Since its discovery in 2009, Candida albicans has caused multiple killings in many parts of the world in just a decade. But what really confuses researchers is the mysterious origin of the fungus and its global transmission path. Given the earliest case reports in Asia, scientists initially speculated that strains in Asia triggered outbreaks in other parts of the world. However, after genetic information comparisons of strains collected from South Asia, Venezuela, South Africa, and Japan, the researchers were surprised to find that they belonged to four separate branches and were not related to each other.
Further comparison of the gene sequences revealed that the four branches were separated from the same ancestor about thousands of years ago and existed as harmless colonies in the environment around the world until the beginning of about ten years ago. Drug resistant strains. That is to say, Candida albicans, which is popular all over the world, appears in different places at almost the same time. Several strains evolve independently in different places, and the possibility of parallel propagation between them is small. What is the reason for them to come out like a good one to be a disaster?
 Regional distribution map of Candida albicans cases
Regional distribution map of Candida albicans cases Regrettably, the exact cause is still unknown. The researchers initially used the cause of drug-resistant bacteria as a reference, and naturally considered that the excessive use of antifungal agents in clinical treatment is the main cause of fungal resistance. However, although there are few types of drugs for clinical treatment of fungal infections, the incidence of fatal fungal infections is actually low, and the application scenarios and drug resistance problems of antifungal drugs are not as common as bacteria.
So, if this pot does not allow the abuse of antifungal drugs to back? What is the cause of the sudden outbreak of Candida albicans? The exact answer is still unknown, however, the pesticide used to kill plant fungi is probably the real reason behind it.
Fungus and human love
Fungi can not only endanger the health of animals, but also harm the normal growth of plants. In the process of crop planting, the use of antifungal drugs is indispensable, and crops such as potatoes, beans, and wheat need to kill pathogenic fungi in the soil regularly. Unlike the names of antibiotics, there are few types of drugs that are resistant to fungal infections, and most of them are azole compounds. The pesticides that kill plant fungi also contain structures similar to those of azoles, which leads to fungal mutations in the natural environment that are likely to occur under the action of pesticides. Once infected, the structure of pesticides is similar. Antifungal drugs will not work.
In fact, human understanding of drug-resistant fungi has reached a tortuous development. Around 1997, a common fungus called Aspergillus fumigatus began to show resistance, and the mortality rate of pneumonia caused by resistant Aspergillus fumigatus was as high as 60%. At first, medical workers naturally believed that the use of antifungal agents during treatment was responsible for the resistance mutations in fungal strains. The fact that the proportion of drug-resistant strains in total strains in treatment also confirmed this hypothesis.
However, during the study, it was found that many resistant strains were also found in patients who had never been treated with azoles, suggesting that resistant strains existed at the beginning of patients with fungal infections. Accordingly, the researchers began to suspect the existence of resistant strains in the environment, and subsequent experimental results corroborated this speculation.
Researchers found the presence of drug-resistant strains in flower beds, grasses, and air-conditioning systems around the hospital. Drug-resistant strains in soil samples accounted for up to 12%. In addition, anti-fungal demethylation inhibitors (DMI) pesticides similar in structure to medical azoles account for up to one-third of the world pesticide market, while resistant strains have also shown corresponding DMI pesticides. Resistance.
 Fungal colonies in the culture dish, all of which are derived from the soil
Fungal colonies in the culture dish, all of which are derived from the soil Although these observations are not sufficient to conclude that pesticide application is the direct cause of fungal resistance, it can be concluded that there are already a large number of resistant fungi in nature, and their power is comparable to Candida albicans. Fungal infections are mainly caused by invasive immunocompromised populations. When drugs can function normally, infections are quickly suppressed. Once drug-resistant fungi emerge, the limited choices in the “human arsenal†will be stretched, resulting in higher mortality in susceptible populations.
New antifungal drugs will find inspiration from pesticides
In the future, in addition to further exploring the relationship between fungal resistance, antibacterial drugs and pesticides, the development of new antifungal drugs with different bacteriostatic mechanisms is also imminent. However, since fungi and human cells belong to the same eukaryotic cells, there are many links between them. Drugs that kill fungal cells often damage normal human cells, so humans can only be limited from a few human and fungal cells. The difference is to design antifungal drugs. Unfortunately, most of these drugs are no longer effective in killing resistant strains.
However, many scholars have suggested that humans can actually find inspiration from antifungal pesticides. This is because the removal of DMI-based agents, as well as several pesticides, can maintain low levels of human toxicity in the effective killing of fungi. A considerable portion of these pesticides are still in a state in which the sterilization mechanism is not fully understood. Finding inspiration for drug design from these proven antifungal pesticides is a reasonable choice.
 Edible fungi are also a kind of fungi
Edible fungi are also a kind of fungi In fact, drug resistance is a long-standing problem in various chemotherapeutic fields such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, antifungal drugs, antiparasitic drugs and even anticancer drugs, and it is an unavoidable fate. We must understand that the game between humans and microbes will be a long-term and escalating battle. In this process, we must use antibacterial agents reasonably, and avoid the drug resistance caused by improper application of drugs. At the same time, we need to include the entire ecosystem of humans and pathogenic microorganisms within the scope of research and discussion.
JRT usb interface distance sensor board adds a USB port to a Laser Distance Sensor, inexpensive laser distance measurement sensors, allowing customers directly using GBeacon-2.3-Fx.exe software to control the rangefinder sensor. Usb laser distance sensors are the the most popular model devices, it works by measuring the phase of an visible-red laser beam that reflects on the target. Usually, customers would like to choose CH341SER.EXE version to test.
USB Laser Distance Sensor,Distance Sensor,Laser Distance Sensor,Distance Measurement Sensors
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.rangingsensor.com