In the past two decades, Novartis has been known for its innovative drugs and mergers and acquisitions, and has achieved great commercial success. But what should be seen at the same time is that digital innovation is also an important direction of its exploration - internal management digital, business data insight, AI + drug discovery, digital tools empower patients, Novartis has been at the forefront of digital innovation.
Novartis history: the chemical giant spanning three centuries turned gorgeously
The history of Novartis is a history of mergers and acquisitions. In 1996, Swiss chemical giant Ciba-Geigy merged with Sandoz, and the newly formed company was renamed Novartis (meaning "new technology" in Latin). Going forward, Ciba, Geigy, and Sandoz each have a history of more than 100 years. The three companies' main businesses have certain overlaps, including dyes, textiles, chemical products, and pharmaceuticals.
Historically, in response to competition from chemical companies in the United States and Germany, Ciba, Geigy, and Sandoz formed a short alliance in 1918 to form Basel AG, which collapsed in the 1950s, after which Ciba and Geigy merged in 1971. In the end, in 1996, the three companies came together again.
Novartis development history
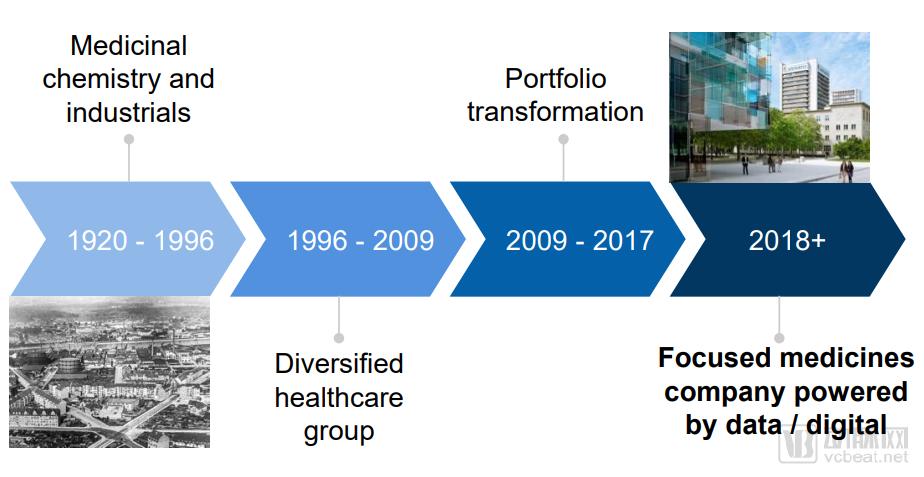
Source: Novartis Annual Report
In 2000, Novartis was listed on the New York Stock Exchange. To further focus on the pharmaceutical business, Novartis split the agrochemicals and seed company Syngenta in 2000. In the next two years, Novartis once again separated the food and beverage sector and integrated the generics business into an independent division (named Sandax).
After the adjustment in 2014-2015, Novartis's business is divided into three parts: innovative medicine, Alcon (ophthalmology), and Sandoz (mature medicine). The innovative medicine department is further divided into Novartis Oncology and Novartis Pharmaceuticals.
According to Novartis's 2017 annual report, Novartis's annual revenue was 49.109 billion US dollars (+1%), of which the innovative medicine business income was 33.05 billion US dollars (+1%), and Alcon's income was 6.024 billion US dollars (4%). Texa’s revenue was $10.60 billion (-1%).
Novartis has been able to maintain high growth for many years, and there are many factors, including the foundations of the merger of the previous companies, the continuous acquisition of high-quality assets, the generic drug business, the special needs of products, and product upgrades.
At the time of the merger, Novartis was already a chemical industry and pharmaceutical giant with sales of 36.2 billion Swiss francs, total assets of 58 billion Swiss francs, and 19 billion in cash and cash equivalents. Adequate funding also laid the foundation for Novartis' continued expansion.
More importantly, Novartis has the ability to continue to launch “blockbustersâ€, including Valsartan (listed in 1997), Imatini (Gleevec) in 2001, and Gilenya (later). Fingolimod), Cosentrx (Secukinumab), etc.
These products have brought a rich market return to Novartis. With only valsartan and Gleevec, the cumulative sales of the two products exceeded $100 billion. According to the information of Novartis official website, there are nearly 30 heavy new drugs that have entered clinical phase III, and more than 10 new drugs have entered the approval stage.
Franchising (product agency) is another major feature of Novartis. According to the Novartis Annual Report, its heavy products include Afinitor/Votubia, Arzerra, and Exjade and Jadenu), Farydak, etc., which generate billions of dollars in revenue each year for Novartis. Of course, product improvement and new use of old drugs have also brought great benefits to Novartis.
Another very interesting point is that Novartis is also a shareholder of the pharmaceutical giant Roche, which will receive a significant investment income from Roche every year. In 2016, this revenue was $464 million, and in 2017 it was $456 million.
Digital transformation is one of Novartis' corporate strategies
Novartis believes that digital technology is changing health care industry, research and development affect the whole process of providing medical treatment to doctors for patients from drugs, such as the application of the sensor are helping researchers and physicians phones more patient feedback to treatment, to obtain a more accurate treatment .
On the other hand, the aging of the population, chronic diseases, and increased incidence of cancer have put forward higher requirements for health care services and brought pressure on the health system. These will help promote the application of digital technology in the healthcare industry and bring better medical services to patients and society. One of Novartis' key strategies is to drive digital transformation and strengthen its position in the healthcare sector.
Novartis believes that the application of digital technology will play a role in drug innovation, disease diagnosis, drug research, population aging, and medical service support. First, the emergence of digital technology as a therapeutic aid has also begun to change the traditional medical concept. For example, mobile applications designed to treat drug abuse and help people with diabetes manage the disease have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to combine traditional medicine with digital technology that helps patients follow healthy behaviors, and is expected to improve the quality of care for patients. And therapeutic effects.
Second, digital technology is changing the way doctors diagnose and treat diseases. For example, more and more sensor technologies are helping researchers and doctors collect information about patient health and its response, using statistical methods and artificial intelligence to mine medical data and provide medical advice.
More importantly, digital technology will transform the way drugs are developed, and the combination of data and artificial intelligence will enable complex biological simulations that have been viewed by the FDA as a surrogate for preclinical animal studies to assess the toxicity of potential new drugs. With the popularity of digital tools, they can shorten research time and increase the likelihood that experimental drugs will be safe and effective.
Novartis said in its annual report that driving a digital transformation is an important strategy. “We are looking for new ways to harness the power of digital technologies – including R&D, sales and operations – in all aspects of our business to increase cost effectiveness and efficiency. Special attention is given to advanced analytics. Artificial intelligence and others. Technology can help us extract insights from clinical trials, our daily interactions with doctors, and large amounts of data from other sources."
Novartis Digital Transformation Strategy
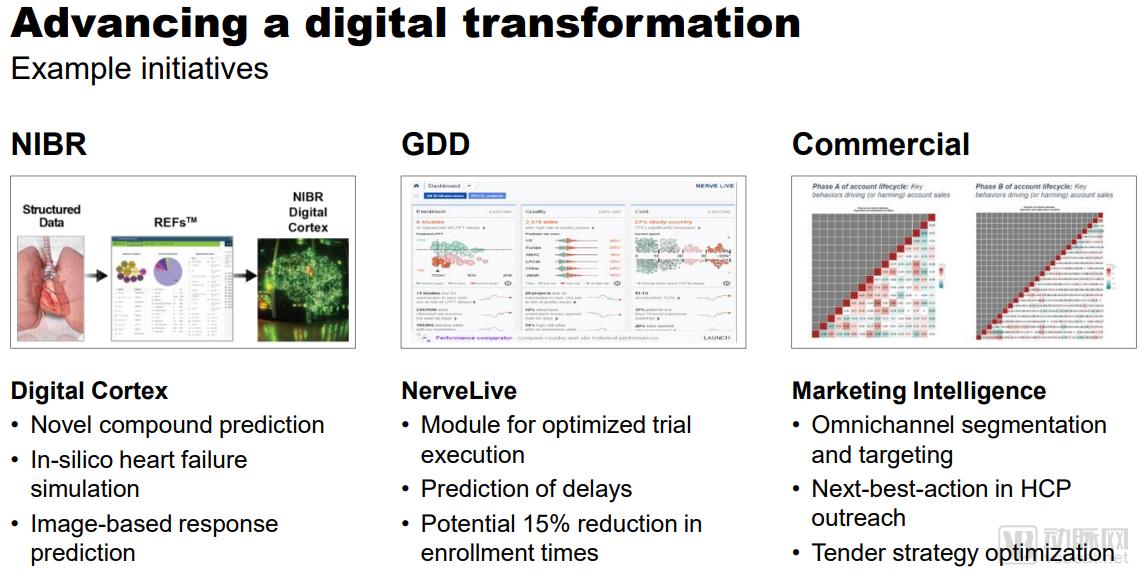
Source: Novartis Annual Report
Below, we will see that Novartis applies digital tools and concepts in all aspects.
Novartis' digital innovation in all aspects
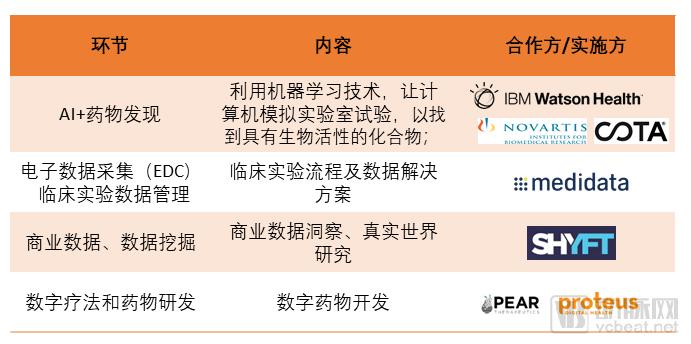
Arterial network mapping
1. Use machine learning and computer vision technology to screen compounds and accelerate drug development
Novartis is using machine learning technology to allow computer simulation labs to be tested, and there are 20 ongoing projects with the goal of reducing the time and resources required while improving drug design.
In an article published in May 2018, Novartis scientists have recently pioneered a special type of machine learning advancement called deep learning that mimics how the eye and brain process visual images. Our eyes perceive light in different tones, and a tightly coordinated neural network transforms these patterns into colors and shapes that we associate with familiar objects, faces and other creatures in our surroundings. Inspired by nature, the Novartis team simulated the same approach and taught how computerized neural networks can recognize subtle changes induced by experimental compounds in cells.
The team initially used supervised methods for deep learning, which meant that they had to teach the system how to identify specific effects in treatment, such as changes in cell shape or protein activity, before the system could identify these effects. They train the network by presenting images of cells treated with compounds known to function in a specific manner in order to learn visual patterns associated with different drug mechanisms. They then tested the cell images using more than 100 mysterious compounds. This research was published on Bioinformatics.
William Godinez, head of the NIBR Infectious Diseases Laboratory, said: "This suggests that the system is likely to shift from digital to biological understanding of the drug's effectiveness in the cell, predicting almost 100% accuracy."
One time-consuming part of drug discovery is the response of a test compound to a diseased cell sample, which typically requires careful analysis of each sample to find a biologically active compound. To speed up the screening process, the team is using machine learning algorithms to identify images to quickly predict which untested compounds might be worthy of further study.
They started with 3,000 compounds, but the ultimate goal was to expand the use of machine learning to screen about 1.5 million compounds in the Novartis compound library.
Machine learning algorithms can also be used to classify various types of medical images during clinical trials and match the characteristics of the data to the patient's response to treatment. These algorithms may then be able to predict future patient response to experimental treatment, providing researchers with information to help them focus their testing on the most beneficial patients.
In addition to independent innovation, Novartis also partnered with IBM Watson Health in June 2017 to use artificial intelligence to improve breast cancer treatment options. A few months earlier, Novartis and Cota Healthcare also had similar cooperation.
It is worth noting that Novartis's huge investment in AI+ drug discovery is not unrelated to Vasant Narasimhan, the new CEO who took over in February this year. He was born in 1976 and graduated from Harvard Medical School. He is very respectful of new technologies. In his tenure as global pharmaceutical development director and chief medical officer, he led the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence in Novartis's drug development and historical data mining.
Now the plan has been extended, led by Achim Plueckebaum, Head of Global Drug Development IT at Novartis, who and his team designed a new system for Novartis Global Drug Development (GDD), which will be available within 18-24 months. The information systems, data and management are migrated to the new system.
This program is what Plueckebaum calls “open thoracic surgery†and has a codename STRIDE – Systematic Transformation Initiative for Development Excellence. The system's capabilities include a submission and file management system, a new research portal, a new high-performance computing environment, and a new system such as the New Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS). These systems can also communicate with each other to facilitate data calls.
After STRIDE is completed, there are two new tasks to be launched – Nerve Live and 42. Nerve Live is a predictive analytics platform that applies analytics and machine learning algorithms to clinical trials. Novartis is working with American machine learning company Quantam Black. Improve the platform; the concept of 42 comes from the "Galaxy Roaming Guide", which refers to the creation of a data set to provide solutions for intractable diseases.
2. Digital transformation of clinical research and market data analysis
At the end of July, Novartis announced a partnership with the company's SHYFT, which consists of two main components:
l STRATA data platform for aggregating and managing an increasing number of third-party and proprietary business data sources;
l LUMEN Insights Platform extracts value from historical data and provides guidance for business activities.
Novartis' partnership with SHYFT has expanded its existing partnership with Medidata, which provides digital solutions and tools for clinical trial management. Together with SHYFT's market data, Novartis's efficient use of data extends from clinical to market.
3. Digital therapy and drug development
In March of this year, Novartis teamed up with Pear Therapeutics to develop a new prescription digital therapeutic drug designed to effectively treat diseases and improve the clinical outcomes of patients.
This cooperation is mainly in three aspects:
Novartis and Pear Therapeutics collaborate on prescription software applications for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia and multiple sclerosis;
Collaboration combines Novartis' leadership in biomedical research and clinical development with Pear's expertise in digital therapy;
Novartis continues to use emerging digital technologies to strengthen research and development and provide better treatment for patients.
Novartis invested in Pear Therapeutics as early as Pear Therapeutics A and B rounds of financing. Pear Therapeutics also said that Novartis has been paying attention to them since the beginning, and the cooperation between the two companies is very harmonious.
Pear Therapeutics is currently the most mature product called ReSETTM. ReSETTM is the first FDA-approved electronic drug for the treatment of drug abuse disorder (SUD). Let patients regain control of drug addiction. Can assist in a range of stimulant-dependent, marijuana, cocaine or alcohol-dependent treatments. Although it has passed FDA certification, it has not yet been commercialized and is still being tested.
In fact, in 2013, Novartis invested in a similar company, Proteus Digital Health, which manufactures an FDA-approved, embeddable sensor to track patient compliance and Research solutions for the treatment of two-way disorders and schizophrenia.
Novartis digital innovation, a hundred years old shop rejuvenation
Novartis announced in August 2017 that Bertrand Bodson will be appointed as the company's chief digital officer. Bodson will be responsible for developing and implementing a company-wide digital transformation strategy, including embarking on ways to improve the company's use of data in drug discovery and development, with patients and doctors. Work with other stakeholders and automate business processes.
Bodson previously worked for EMI Music, Sainsbury's Argos and other companies, and during his tenure, he successfully converted Sainsbury's Argos from a traditional retailer to the UK's third largest online retailer. The establishment of the position of Chief Digital Officer represents the determination and execution of Novartis's attempt to digital transformation.
The “magic†of innovative pharmaceutical companies is actually very simple, find a new drug and quickly commercialize it. The biggest influencing factor is the speed of “finding†new drugs and the ability to commercialize.
Driven by new technologies such as biotechnology, genetic editing, and artificial intelligence, the way to “find†new compounds and commercialize is changing. Novartis hopes to adapt to this change and maintain its dominant position in the healthcare field. Digital transformation is an important direction of Novartis. This concept has also penetrated Novartis's R&D, clinical and patient services, and is waiting for the outcome.
Straight Wafer Ice Cream Cone,Cylindrical Wafer Cone Products,Wafer Cones For Soft Ice Dressing,Low Sugar Wafer Cone
Tianjin Yongkang Food Co., Ltd , https://www.yongkangfood.com