Recent studies have shown that deep cranial stimulation promotes dopamine activity, and it is this neurotransmitter involved in motivation and pleasure that enhances the body's ability to glucose metabolism. Related research was published in the May 23 issue of Science Translational Medicine.
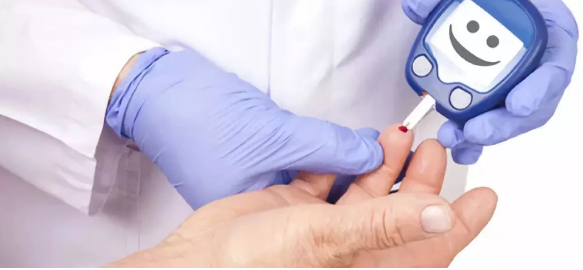
In the Netherlands, there was a man who asked the doctor for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), so the doctors suggested a newer but promising treatment: the electrode Implanted into the brain to perform deep cranial stimulation of related brain tissue. This treatment is indeed effective, but it also has unintended side effects - the patient's type 2 diabetes seems to improve.

In order to test whether the patient was really improved because of deep cranial stimulation (the required insulin injection volume was reduced from 226 international units to 180 international units per day), endocrinology at the Amsterdam Medical Research Center in the Netherlands Mireille Serlie and her colleagues asked the patient to participate in an experiment involving 14 other men and women who had a deep cranial electrode with OCD (no diabetes). Serlie and colleagues turned off the electrode device for 17 hours and measured the subjects' fasting blood glucose levels and insulin response, and found that deep cranial stimulation did significantly increase insulin sensitivity in all subjects.
Mike Michaelides, a neuroscientist at the National Institute on Drug Abuse in Baltimore, Maryland, said that such a pathway was previously found in mice, and the study first found a similar pathway in humans. It is unrealistic to apply this deep cranial stimulation to all diabetics, but less invasive neurotherapy with dopamine as a target may be feasible in the future.
Diabetes is caused when glucose in the body's blood circulation system is maintained at a high concentration for a long time. Type I diabetes often begins in childhood, and the pancreatic cells responsible for insulin production are destroyed. Insulin is a hormone that promotes the metabolism of cells in the body. Type II diabetes is induced by a series of causes, including susceptibility. Gene combinations, poor eating habits, lack of exercise, etc., all of these factors can destroy the body's ability to produce insulin. As time goes by, the task of blood glucose elimination by cells is becoming more and more difficult, and people are increasingly required to maintain a large amount of insulin to maintain blood sugar stability. Both types of diabetes are difficult to cure.
Mouse studies have shown that dopamine released by stimulation of ventral striatum neurons in the brain plays an important role in the regulation of blood glucose, which is often associated with decision-making mechanisms. To investigate whether the body also has a similar glycemic regulation mechanism, the Serlie team administered drugs that reduced dopamine levels to 10 healthy testers, resulting in reduced insulin sensitivity in all subjects, further supporting previous conclusions.
The team also used optogenetics to stimulate the striatum neurons of mice to modulate neuronal activity. When nerve cells release dopamine, the amount of sugar that other cells take up from the blood increases. Michaelides said the mouse study further confirmed the findings of his own and other team studies, and suggested that the dopamine pathway in the nucleus accumbens (part of the striatum) is critical in glucose metabolism.
Nima Saeidi, a surgical assistant professor at Harvard Medical School in Boston, points out that targeting deep-cranial stimulation or other means of targeting the dopamine pathway in the brain may not be an effective treatment for most people with diabetes because of prolonged exposure to hyperglycemia. High insulin environment may cause large changes in the function of cells and organs. “The results described by the author in the research article probably do not apply to people with diabetes,†Saeidi prompts. Serlie agrees that for some people, cell damage is irreversible, but she says that this method does improve the efficiency of existing insulin use in the early stages of the disease.
α- GPC is a water-soluble substance with two fatty acids removed from the main phospholipid PC (phosphatidylcholine) constituting the cell membrane.α- GPC is a water-soluble substance with two fatty acids removed from the main phospholipid PC (phosphatidylcholine) constituting the cell membrane.
Originally widely existing in organisms, it is one of the body components existing in human breast milk and body fluids. Research in the food industry shows that GPC can be obtained by removing fatty acids (deacyl) in the structure with PC in soybean lecithin as raw material. In the revision of food and drug classification in 2009 α- GPC (sn-glycerol-3-choline phosphate) is defined as food.
Purpose: brain health food. It is clinically used to prevent and treat atherosclerosis, fatty liver, neurasthenia and malnutrition. It can also be used as an additive for food, cosmetics and pharmaceutical excipients. It can be transformed into hemolytic lecithin by phospholipase a.
Prevent choline deficiency, increase neurotransmitters and promote the secretion of growth hormone. Although both eggs and eggs contain choline, it is confirmed that the uptake in the form of GPC is faster than the absorption through the portal system, and it is easier and more efficient to convert to choline. And GPC is one of the few five that can pass through the blood-brain barrier, so it can be quickly converted from choline to acetylcholine.
Alpha GPC Powder, 9-Fluorenol Powder, Phenibut Powder, Tianeptine Sodium Powder
Xi'an Tian Guangyuan Biotech Co., Ltd. , https://www.tgybiotech.com